Introduction
This research aims to develop a system to support and assist vocational learners in the High Vocational Innovation Scholarship Program who are at risk of leaving school by fostering their physical and emotional well-being.The current era is characterized by the widespread use of digital technology, which seeks to stimulate economic growth through innovation and contemporary technology to advance the country's development. This trend is sometimes called the trend to introduce new services. In the digital age, that is called "disruptive technology" because it brings about significant changes in various aspects, including education(Loos & Ivan, 2022). Technologies have great potential to drive innovation and competitive advantage and motivate the push for digital transformation in response to the expansion of technologies and media formats, including new communication systems that connect populations around the world (Solberg et al., 2020). Technological advancements have led to progress in the dissemination of information and news. It profoundly impacts several facets of society, including economics, politics, culture, education, public health, and the environment. Thailand is among the nations affected by this swift transformation, significantly altering lifestyle patterns. Human resource development has undergone a significant transformation compared to previous times (Jindanilet al., 2022).
The volatile circumstances that have occurred have had a profound effect on students in numerous countries, including Thailand, particularly in terms of personal safety, such as the perils associated with drug use. Social media fraud poses a risk of bodily harm and promotes violence. Additionally, it hurts students' mental well-being. Societal issues and uninspiring surroundings significantly impact children and adolescents in contemporary society, leading to a deviation in their behavior compared to previous generations. Despite the efforts of parents, teachers, and child workers, their love and goodwill alone are insufficient to provide complete protection. To ensure the safety and conformity of children and youth to societal norms, it is crucial to address the disparities in educational possibilities and variations in educational quality. Thai education management faces challenges such as the distance and inefficiency of small schools, as well as governance issues.As social origin decreases, parental attitudes appear to be more important (Prasarn, 2019). Greater heterogeneity in educational systems, coupled with increased teaching time, limits the impact of social origin on student performance. Independence in higher education increases the effect of parental influence (Ammermueller, 2005).
The inequality dilemma, a persistent affliction of Thai society, is escalating in severity. The disparity between the rich and the poor is increasing. Poverty and inequality are prevalent worldwide, as indicated by the national average norm. It is the primary global issue. For this reason, The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) gives this issue significant importance and views it as a means of eliminating poverty. The primary objective of education is to alleviate poverty. Education must exclusively focus on providing high-quality education. Consequently, it will aid in eradicating poverty and promoting optimal health (Thippaporn, 2021).Stockhammer (2015) argues that rising inequality should be considered the root cause of the current crisis. Rising inequality puts downward pressure on aggregate demand as lower-income groups tend to consume more marginally, and rising inequality leads to higher household debt as working-class families try to maintain social consumption norms even as real wages stagnate or fall. Rapid technological changes have resulted in unequal access to education. Students from low-income families or remote areas may not have the same access to technology as those from high-income backgrounds, creating significant learning gaps. Students with strong technology skills can adapt well to digital learning environments.In contrast, those who are less familiar with technology may struggle and lack confidence, increasing their risk of dropping out, and this disparity ultimately contributes to higher dropout rates among students.
Student dropout is a significant concern in the country's education administration, leading to the government's inefficient allocation of funds for educational infrastructure. Addressing this problem promptly is critical to preventing and resolving it. This aligns with the findings of Phochchong and Cheerapatdhanadhorn(2021), who define dropout as the premature termination of education without completing the required coursework and the waste of educational resources. Additionally, Phannaratet al. (2009) conducted a study that revealed that students often choose to drop out to secure employment and financially support their families, viewing it as a necessary step for their survival in society. Lee and Choi (2011) state that influenced students’ decisions to drop out and classified them into three main categories: (a) student factors, (b) course/program factors, and (c) environmental factors. Students from more disadvantaged socio-economic backgrounds may have worse skills, poor study habits, and a lack of critical thinking, all of which may negatively affect motivation and academic achievement, increasing the risk of dropping out (Aina, 2013).
Ensuring student retention from enrollment to graduation is a critical concern that educational institutions must prioritize. The student support system is crucial due to its well-defined procedures, methodologies, and instruments that adhere to high-quality standards, with verifiable evidence of its effectiveness. The advisor is the primary individual in charge of the business. All individuals associated with the educational institution, including parents, administrators, and teachers, actively engage in promoting, fostering, safeguarding, and resolving issues to facilitate students' holistic development, encompassing their optimal potential, desirable attributes, robust mental resilience, high-quality life, and the ability to navigate and overcome any crises. In addition to delivering education, we strive to prevent and tackle various issues while also bolstering and empowering students. In 2021, the Office of the Basic Education Commission reported a failure to complete the education system before graduation(Korop& Rupan, 2021). A support system can provide problem-solving outcomes based on specified criteria and can assist students (Arifin & Saputro, 2022). Students who frequently use student support services and counseling have a higher social adjustment. Finally, students who are better able to adjust to college life are more likely to be committed to their college goals and have a higher commitment to the university (Grant Vallone et al., 2003).
Therefore, it is important toensure that students receive prompt and accurate care and support, meeting their needs holistically. Enhance their life skills by offering guidance and assistance, particularly to youth from troubled family backgrounds. This involves fostering partnerships among parents, communities, and relevant organizations (Casanova et al., 2018).Consistent with this, vocational education issues are also a determinant factor for student persistence and dropout, particularly career motivation and student-defined goals. There is a harmonious and collaborative effort among all parties, both within and beyond the institution. When it comes to encouraging morality, teachers and educational workers need to address behavior problems effectively. Additionally, they should prioritize addressing the issue of drug abuse in schools and implement a validated quality system. Providing close and thorough care and assistance to students in a timely and correct manner. Strengthen life skills by giving advice, providing care, and assisting students who are in families experiencing problems or disadvantaged families. By focusing on the development of parents' networks, communities, and related agencies. There is coordination and cooperation of all parties, both inside and outside the school, in promoting morality and solving teacher behavior problems,educational personnel, and students.Take immediate action to address the drug issue in schools and implement a robust system that can be validated for its effectiveness.
The Equitable Education Fund's strategy is to promote the development of comprehensive support systems and ensure scholarship recipients' well-being. This would successfully enhance the quality of life and academic performance of the scholarship recipients. The education system needs to develop youth with vocational and life skills, preparing them for employment and contributing to the creation of strong, sustainable communities.Develop tactics to reduce the loss of scholarship recipients. Promote educational equity and minimize educational inefficiency by ensuring all students have equal access to learning opportunities. Enhancing one's ability to effectively compete with other countries is crucial. It exerts a tangible and efficient impact on economic progress.
Methodology
This research employs both quantitative and qualitative methods. To gather quantitative data, a questionnaire was distributed to solicit opinions from students. For qualitative data, insights were obtained through discussions between teachers and administrators aimed at developing a comprehensive system to support vocational students in the High Vocational Innovation Scholarship Program who are at risk of dropping out. The research methods are outlined as follows:
Participants
1. The target population for quantitative research consists of the students enrolled in the High Vocational Innovation Scholarship Program, Equitable Educational Fund (EEF). Specifically, 217 students withdrew from 31 educational institutions who pursued their studies from 2019 until 2023.
2.Teachers and administrators in educational institutions participating in the High Vocational Innovation Scholarship Program make up the target demographic for qualitative research, which aims to extract valuable insights from their work. The Fund for Educational Equality has a presence in 30 sites, with one person assigned to each location, resulting in a total of 30 individuals.
ResearchProcess
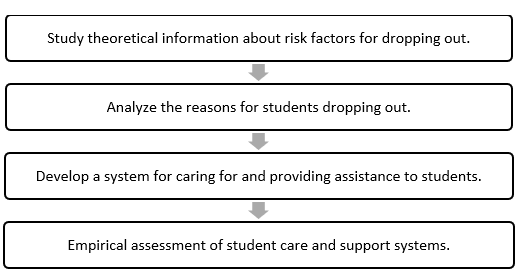
Figure 1. Process of Establishing a Support System for Vocational Students at High Risk ofDiscontinuing Their Education
The following provides a comprehensive breakdown of each stage in the research process.
1. Analyze data from papers and related studies to explore the theoretical information regarding the causes of dropping out. We can deduce that five factors contribute to dropping out, specifically 1) the process of teaching and learning, 2) proximity to loved ones, 3) surroundings, 4) technological availability, and 5) physical and mental well-being.
2. Examining the factors that contribute to student attrition. The researchers established a mechanism for gathering data on scholarship recipients who discontinued their studies by utilizing the five rationales who pursued their studies from 2019 until 2023.
3. Establish a comprehensive system of care and assistance for students, which includes a variety of components and involves providing support. These factors may include the involvement of family, friends, and other close individuals. The use of information technology systems in educational institutions encompasses a variety of elements, including student health care management. By assessing academic performance based on productivity, including lowering dropout rates, within the teaching and learning management framework.
4.conducted an empirical evaluation of student care and support systems, focusing on four key areas: correctness (measured by the Accuracy Standard), appropriateness (measured by the Propriety Standard), feasibility (measured by the Feasibility Standard), and usefulness (measured by the Utility Standard). (Stufflebeam & Shinkfield, 2007) assessment model guided this study.
Research Tools
This study utilized two sets of data collection instruments: a causal questionnaire to investigate the reasons for dropout among scholarship students in the educational system, and a comment form to facilitate knowledge exchange and provide support to scholarship students in the care system. The specifics of each tool are as follows:
1. The questionnaire's purpose is to identify the reasons why scholarship students drop out of the educational system. The questionnaire consists of five elements: 1) the teaching process; 2) close people; 3) the environment; 4) access to technology; and 5) physical and mental health.
2.Form for gathering feedback on the student care and aid system, emphasizing individual viewpoints and encouraging unstructured communication. The comment form scrutinizes the study's data and tackles topics related to student care and support. The system will comprise four components: 1) Living care; 2) dropout protection; 3) counseling and advice; and 4) transfer to support.
3. The system evaluation form for empirical student care and assistance focuses on four aspects: correctness (measured by the accuracy standard), appropriateness (measured by the propriety standard), feasibility (measured by the feasibility standard), and usefulness (measured by the utility standard). The assessment form possesses distinct attributes and functions as an approximate measurement scale. The rating scale has five distinct levels.(Papanai& Poolkrajang, 2023).
4. Creating and ensuring the quality of tools. Examine pertinent papers, concepts, theories, and research to identify appropriate interview inquiries. Experts should then receive the material to assess its content validity and determine the Index of Consistency, also known as the Index of Item Objective Congruence (IOC)(Poolkrajang & Papanai, 2024).The expert evaluation yielded a congruence index value of 0.80, exceeding the specified criteria. We should then integrate the feedback from the validators. Let's enhance and rectify it to augment the tool's comprehensiveness.
Data Collection and Analysis of Results
Data collection from the target group defined from the quantitative and qualitative groups from educational institutions that received funding. educational equality and scholarship to students who dropped out of school and studied from 2019-2023.
Data Analysis
Quantitative Data Analysis
This analysis focuses on responses to a questionnaire regarding the reasons scholarship students drop out. It includes frequency distribution, percentage, and evaluation of the student care and support system using statistical measures such as mean (x̄) and standard deviation (S.D.). The evaluation is conducted in four aspects: accuracy standard, proprietary standard, feasibility standard, and utility standard. The responses are rated on a 5-point Likert scale with the following criteria:
Average 4.50-5.00: Indicates the student care and support system is at the highest level.
Average 3.50-4.49: Indicates the student care and support system is at a high level.
Average 2.50-3.49: Indicates the student care and support system is at a moderate level.
Average 1.50-2.49: Indicates the student care and support system is at a low level.
Average 1.00-1.49: Indicates the student care and support system is at the lowest level.
To judge the effectiveness of the student care and support system, an average score of 3.50 or above with a standard deviation of no more than 1.00 is considered acceptable.
Qualitative data analysis
Qualitative data was analyzed through content analysis, which involves summarizing information gathered from interviews and questionnaire responses by carefully checking. After that, the information wasobtained to organize a meetingwith 30 teachers and administrators in educational institutionsparticipating in the High Vocational Innovation Scholarship Program to exchange opinions on the causes of scholarship student dropouts to develop a more efficient care and support system.
Integration of quantitative and qualitative research
This section integrates both quantitative and qualitative research methods. A questionnaire was used to gather opinions from teachers and administrators, complemented by interviews and knowledge exchange meetings. The overall evaluation of the student care and support system was derived from both qualitative analyses and quantitative evaluations.
Results
Developing a system for care, and assistant vocational students in the High Vocational Innovation Scholarship Program who are at risk of dropping out. There are two phases of research results: studying the reasons for dropping out of scholarship students and developing a care and assistance system.
Results of Causes of Scholarship Students Dropping out According to Risk Factors
Table 1. The Reasons for Dropping out of Scholarship Students
| Group 1 Teaching and Learning Process | |||
| In case of falling out | Quantity | Cause | |
| 1. Students have academic performance below the standard. | 133 | 1. Students do not understand the content learned. | |
| 2. Students lack motivation to study. | |||
| 3. Students whose academic performance is lower than the standard continuously. | |||
| 4. Students cannot keep up. felt branch and subjects that are difficult to study | |||
| 2. Students have continuous negative behavior. | 62 | 1. Students know that they are lazy. But there was no improvement in their own behavior. As a result, students do not complete professional experience training. | |
| 2.1 Absenteeism behavior | 2. Students do not like the teaching style of the teacher. | ||
| 2.2 Behavior of lacking participation in activities | 3. Students lack regular participation in ongoing activities. | ||
| 4. Students do not want to study, are lazy, and miss class regularly. | |||
| 3. The student has undesirable behavior. Not ready to study | 2 | Students do not like the agricultural field of study. | |
| Group 2 Close people | |||
| In case of falling out | Quantity | Cause | |
| 1. Unwanted behavior, being attached to boyfriend or girlfriend | 6 | 1. Having problems with family Because I want to get married But the family still doesn't agree. As a result, the student had to flee home to meet his girlfriend. | |
| 2. The student is addicted to his girlfriend. Absent from school in a row. | |||
| 3. The student has romantic behavior cause problems. | |||
| 2. Behavior of being attached to friends | 1 | Students have a habit of being attached to friends. Not attending class as scheduled When they are behind in class, the students' academic performance is lower than the standard. | |
| 3. Pregnancy during school age | 2 | During the school break, the student became pregnant. Therefore, it is necessary to leave the education system halfway. | |
| Group 3 Environment | |||
| In case of falling out | Quantity | Cause | |
| 1. The student has undesirable behavior. | 3 | Students are involved in drugs and vices. | |
| 2. Termination of student status | 1 | The student is involved with drugs. Convicted of drug crimes. | |
| 3. Students have continuous negative behavior. | 1 | Because both parents of the learner have died. As a result, students are frequently absent from class. | |
| Group 4 Access to technology | |||
| In case of falling out | Quantity | Cause | |
| 1. Unwanted behavior | 4 | 1. Students are addicted to games and have academic results below the standard. | |
| 2. Students are involved in vices, gambling. | |||
| 3. Students buy a phone by paying in installments and have academic results below the standard. | |||
| Group 5 Physical and mental health | |||
| In case of falling out | Quantity | Cause | |
| 1. Physical health problems | 2 | 1. Students have not completed professional training. This is because students often have stomach aches. Is suffering from interstitial cystitis and is unable to function continuously. | |
| 2. Students have not completed professional training. Because the student is sick with otitis media. If you are in a loud place, you will have blood coming out of your ears. | |||
| Total | 217 |
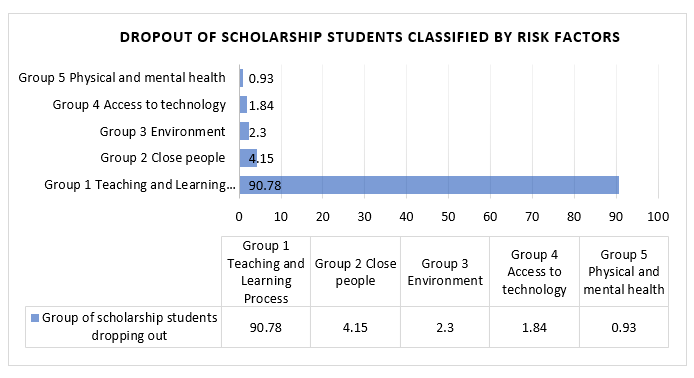
Figure 2. The Number of Scholarship Students Dropping out
From Table 1 data and graphic charts (Figure 2) of the educational system classified by cause, it was found that 217 scholarship students from general educational institutions dropped out of the education system, with the order of risk causes as follows:
The primary factors contributing to issues in the teaching and learning processes are absenteeism, inappropriate behavior, and personal dissatisfaction with the teacher.
Number I: strongly dislike the course of study, specifically accounting, with a dissatisfaction level of 90.78 percent.
Number 2: Researchers identified factors related to close relationships, such as friends, romantic partners, individuals of the opposite sex, infidelity, and teenage pregnancy 4.15 percent of respondents cited physical health as their reason.
Number 3: A cluster of environmental factors, such as family, community, substance abuse, and surroundings, can significantly impact children. Calculating the total as 2.30 percent.
The fourth group of causes in the story pertains to access to technology, including social media usage, visiting websites, playing games, and indulging in luxury.
Number 4: Vices and gambling account for 1.84 percent of these causes.
Number 5: A collection of factors that contribute to both physical and mental well-being, including stress, depression, and hereditary disorders, which make up 0.93 percent.
In summary, risk factors for student withdrawal obtained from questionnaires of teachers and related persons include absenteeism from class, inappropriate behavior, disliking teachers, disliking the subjects being studied, quarrels with friends, lovers, friends of the opposite sex, having affairs, being pregnant at school age, working to support the family, drug addiction, having problems in the community and environment that affect the learner, being addicted to games, spending money extravagantly, being addicted to vices and gambling, and physical and mental health problems, being stressed, being depressed, and having chronic diseases.
Guidelines for Solving the Problem of Student Scholarship Dropping out
Table 2. Guidelines for Solving the Problem of Scholarship Students Dropping out
| Scholarship students dropout of the education system | Guidelines for solving the problem of dropping out of the educational system of scholarship students |
| 1. Teaching process | 1. Organize activities to enhance knowledge, skills, and the aims of education. |
| 2. Develop knowledge and teaching styles for teachers. | |
| 3. Strengthen attitude Personality for students. | |
| 4. Provide supplementary teaching in cases where students have poor academic performance. and interested students. | |
| 5. Create a source of knowledge for students. | |
| 6. Create rules and regulations for student behavior. | |
| 7. Develop competencies for teachers and students. | |
| 8. Organize activities to create understanding between students and teachers. | |
| 9. Organize activities to increase motivation. Awaken the power to conquer goals in students. | |
| 10. Provide guidance and guidelines for improving academic performance. | |
| 2. Close person | 1. Organize activities to enhance knowledge about sex education. and appropriate behavior for learners. |
| 2. Track and process student behavior. | |
| 3. Adjust attitudes and provide appropriate behavioral guidelines for learners. | |
| 4. Arrange special learning times for students who are pregnant during school age. | |
| 3. Environment | 1. Meeting with parents to inform them of the details and objectives of the Equitable Education Fund project. |
| 2. Improve understanding between parents and learners. Provide consultation and close supervision. | |
| 3. Organize knowledge training activities on The dangers of drugs. | |
| 4. Monitor and process student behavior. | |
| 5. Organize activities with the community to develop and enhance the environment within the community. | |
| 4. Access to technology | 1. Organize activities to enhance knowledge and financial skills. |
| 2. Organize money saving activities. | |
| 3. Strengthen knowledge and skills in generating income while studying. | |
| 4. Monitor and process student behavior. | |
| 5. Physical and mental health | 1. Assign a supervising teacher to give advice and closely monitored. |
| 2. Monitor and process student behavior. | |
| 3. Organize behavior-melting activities Recreational activities to reduce stress and pressure of students. | |
| 4. Create applications, channels, and spaces to prevent students feelings. | |
| 5. Collaborate with government agencies, the private sector, psychiatrists, and experts. | |
| 6. Health check and mental health assessment. | |
| 7. In case of emergency, refer to experts for treatment. |
Table 2 Findings suggest that addressing the issue of dropout among scholarship students in the education system requires focusing on five key areas: the teaching and learning process, the student's social environment, access to technology, and physical and mental health. We recommend implementing a student support system within educational institutions that includes teacher advisors, to tackle this issue. Students must convene every week. It is important to closely monitor pupils who are struggling academically. These students should receive additional educational support from the school. Each department should have a parent network system at its core, along with corresponding activities. This will enhance the ability of students in the at-risk category to focus on their studies, including engaging in peer-to-peer activities. Engage in recreational activities at home to alleviate stress. Furthermore, it is imperative to adapt the teaching and learning methods to encompass a wide range of perspectives. Implementing activities that foster a comprehensive understanding of sex education and acceptable conduct among learners can help achieve this goal. Additionally, it is crucial to conduct training sessions that educate students about the potential risks associated with drug use, among other topics. These ideas are one of the main strategies to decrease the dropout rate among students in vocational education.
System Development Results in Caring and Supporting Vocational Students
The participants suggested that implementing a student care and support system in all vocational education institutions could effectively prevent student dropout. This system would involve living care, dropout protection, counseling and advising, and transfer to support. Data from both quantitative and qualitative analysis of participant responses revealed four crucial components within a student care system for at-risk vocational students, as illustrated in Figure 3.
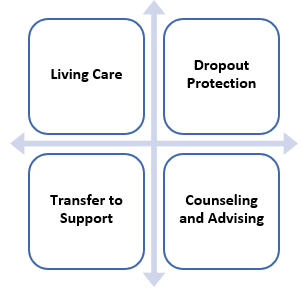
Figure3. System of Student Care for Vocational at Risk of Dropout
Component 1: Living Care
1) The student care committee functions as a committee to facilitate the involvement of all stakeholders in the planning, supervision, follow-up, and consideration of students' well-being, including scholarship students and co-government members. Its primary focus is on providing care and warmth and ensuring the safety of students. While within the educational institution, and occasionally outside of it, providing guidance on student conduct entails adapting to societal norms and regulations, as well as the cultural traditions of the institution. This involves planning strategies to prevent, manage, and resolve instances of undesirable behavior among students, including collaborating with parents and ensuring the follow-up on corrective measures for inappropriate conduct.
2) Hostel supervision: educational institutions should employ teachers to oversee hostel operations. Teachers should supervise the dormitory's management to meet its goals. Certain educational institutions have a "dormitory constitution" that enables students to collaboratively establish regulations or constitutions for their dormitories. Establishing different criteria for each dormitory is crucial. Certain educational institutions employ dormitory instructors or facilitator-dormitory teachers (Teacher Fa-D), whose primary responsibility is to ensure the well-being and welfare of the students. Students who receive scholarships and live in dormitories develop essential life skills. Living harmoniously with friends fosters knowledge cultivation and generosity towards one another. Acquire knowledge about methods to conserve and uphold cleanliness. I oversee the education of students residing in the dormitory, ensuring adherence to safety, cleanliness, landscaping, and the preservation of cultural and traditional norms.
3) Home visits for students to foster and enhance student development, it is crucial for teachers to be acquainted with the personal and familial circumstances of their pupils. To enable teachers to comprehend the precise causes and issues faced by pupils, it is important to consider factors such as family traits and the students' living environment. Engaging in-home visits with students is an effective way to resolve issues. This will allow teachers to gain a genuine understanding of a child's family and living circumstances. Educators learn about parental perspectives on educational establishments, instructors, and students. This fosters a positive rapport between educators and caregivers. Facilitate the transmission of student information between instructors and parents during home visits by adhering to suitable principles. Home visits are an exceedingly beneficial exercise. It enhances teachers' comprehension of students. Additionally, it involves acquiring knowledge from one another. It facilitates the establishment of strong ties among educational institutions, teachers, and parents. This will be beneficial for student advancement and growth. In the distant future, it is crucial for educational institutions to persistently focus on this topic to fully exploit the benefits of this activity. We must adhere to rigorous and suitable guidelines.
Component 2: Dropout Prevention
1) By using a student name verification system to verify the accuracy of student names. Currently, there are numerous formats available for this purpose. Initially, it involved merely verifying names on a document. The student’s name check method is convenient for both teachers and parents. Students enter and exit the school premises daily. It can condense student enrollment and withdrawal data. Education and other fields can individually employ technologies such as RFID, barcode, finger scan, and SMS systems to promote student growth by categorizing them based on different qualities.
2) Strategies to mitigate issues such as substance abuse, infidelity, and gambling. Currently, there is a growing prevalence of drug use among young people. The use of drugs results in detrimental consequences for the nation, both in the present and in the long term, due to the physical and mental harm they inflict on users. Engaging in destructive behavior can have detrimental effects on one's physical and mental well-being, making it difficult to function in society. Young people who exhibit such behavior and desire to experiment may feel the need to seek acceptance by joining a group of friends. This desire to fit in and imitate their peers can lead to the misuse of free time, making them vulnerable to drug abuse. Furthermore, engaging in negative activities within the group can lead to conflict and other negative consequences. Property offenses occur after sexual encounters. Hence, to avert potential issues that can arise for scholarship recipients, educational institutions should collaborate with all relevant stakeholders. Every societal group actively participates and initiates a campaign to combat drug abuse. The campaign aims to disseminate knowledge to young individuals, including school-age children and teenagers, while also fostering information and awareness among parents. Encouraging community and social engagement. This will yield beneficial outcomes for students and educational institutions.
3) Educational institutions offer remedial courses to students who have performed poorly academically during their studies. These courses are conducted by educational institutions, with academic teachers assisting them. Remedial teaching is an instructional method that focuses on providing additional support and assistance to students who are struggling academically. Because pupils have varying characteristics, it is necessary to organize alternative instructional arrangements to accommodate these disparities.
Component 3: Counseling and Advising
Student assistance comes in various forms. The outcome depends on the individual's attitude toward either the issue at hand or the individual seeking assistance. Simultaneously, the problem-solving process considers whether the helper resolves the problem alone or if it involves a collaborative effort between the helper and the individual seeking assistance. Counseling and guidance are other means of providing support to students. Counseling aims to achieve four primary goals: 1) Transforming negative emotions into positive ones with rational justifications. 2) Enhancing self-awareness. The benefits of emotional intelligence include 1) understanding and managing one's own emotions; 2) effectively relating to others and the environment; 3) making informed judgments; and 4) implementing decision outcomes suitably, encompassing feelings, behavior, personality, and other aspects.
Nevertheless, counselors are required to possess expertise and undergo training. This can be achieved by following the counseling approach described below:
1) Establishing goals for counseling
2) Gathering information about the individual seeking assistance through various means, such as assessments, interviews, active listening, verbal communication, and other procedures that involve careful observation.
3) Diagnosing issues and forecasting behavior involves identifying the root causes of difficulties faced by individuals seeking advice, using diverse data sources, and projecting their future actions in the absence of assistance.
4) Counseling is a consultation between a counselor and someone seeking guidance. The chosen counseling method aims to promote mutual assistance in problem-solving and decision-making. The choice of approaches employed depends on the individual seeking guidance and the prevailing circumstances.
5) Monitoring and evaluation To determine the level of success, the monitoring and evaluation process assesses the effectiveness and proficiency of counseling and support. In the future, the goal is to improve counseling techniques. To determine their ability to carry out the task efficiently, evaluate the counselor's qualifications and competence.
Component 4: Transfer to Support
Addressing and resolving student issues with the adviser can sometimes be difficult. If your behavior does not improve, we recommend seeking assistance from an expert to help students. To address students' issues, receive prompt and effective assistance. When the counselor or teacher is absent, the problem may become more complicated. Alternatively, it proliferates and evolves into a substantial predicament that poses a formidable challenge to resolve. The counselor may initiate this process by becoming familiar with the students. The counselor categorizes students seeking care and assistance into two groups: individual students and those referred for introduction.
1) Internal forwarding involves documenting the transfer of students to teachers or individuals who assist students, such as guidance counselors or administrative staff. Internal referrals for care and assistance in educational institutions include subject teachers, nursing teachers, and other specialized instructors. For example, in some schools, a classroom adviser known as a facilitator-class instructor teacher (teacher Fa-C) provides support to scholarship students. The purpose of this service is to provide systematic guidance and support to students in various areas, including academics, personal development, social integration, and adjustment to the educational environment. In addition to offering support when students face challenges, our goal is to empower pupils to overcome diverse obstacles and achieve effective learning outcomes. This internal forwarding not only forwards the student's current year of study but also transmits additional information about the student. Upon a student's promotion to a higher grade level, advisors and other pertinent individuals need to compile crucial information to provide comprehensive support.
2) External forwarding: The guidance counselor or administration will send the student to an external specialist. If the guidance counselor or administration receives this information, they will rectify the situation. Those related to student issues present a significant challenge for counselors to address. If there are specific challenges, such as problems relating to intense emotions, aggressive behavior, or a complicated mental condition that requires close support and psychiatric therapy, it is advisable to recommend the individual to someone with specialized expertise who can provide further assistance. The receiver requires structured support. To ensure efficient support, it is necessary to collaborate with appropriate individuals to coordinate tasks. This involves documenting student requests and directing them to external experts via guidance counselors or the administration, with the operator facilitating the process for the students. Get prompt and efficient assistance to resolve issues or help students.
Results: Empirical Evaluation of the Student Care and Support System
An empirical assessment of student care and support systems Evaluated in 4 areas: accuracy (Accuracy Standard), suitability (Propriety Standard), feasibility ( Feasibility Standard), and usefulness (Utility Standard). The results of the evaluation are according to Table 3.
Table 3. Results of the Evaluation of the Empirical Student Care and Support System
| Evaluation List | Mean | D | Opinion Level |
| Accuracy Standard | 4.87 | 0.35 | the most |
| Propriety Standard | 4.57 | 0.57 | the most |
| Utility Standard | 4.90 | 0.31 | the most |
| Feasibility Standard | 4.73 | 0.52 | the most |
| average | 4.77 | 0.44 | the most |
From Table 3, the empirical evaluation of the student care and support system revealed that the overall assessment was quite satisfactory. We carefully examined each facet and found that the utility standard had the highest average score of 4.90, followed by the accuracy standard with a score of 4.87. The feasibility standard and the property standard were ranked next, respectively. The evaluation results met the specified criteria.
Discussion
According to the study,it was found that the reasons for dropping out fromthe educational system depend on risk factors in the teaching and learning process. Most of the reasons come from students not understanding the content they are learning. Learners lack motivation to study. Students have consecutive academic achievements below the standard. Students can't keep up. Feel that the field of study is difficultIn addition, it was found that Learners have continuous negative behavior, such as students knowing that they are lazy. But there was no improvement in their behavior. As a result, students do not complete professional experience training. The students do not like the teaching style of the instructor. The students do not participate in regular activities. and students do not want to study, are lazy, and continuously miss class regularly Accounting for 90.78 percent, this is consistent with the results of the study by Tas et al. (2013).These factors are stated as absenteeism, intensive curriculum, and grade repetition. As can be seen, absenteeism, intensive curriculum, and grade repetition can cause high rates of dropout.Toumtab et al.(2020) state that students lack participation in activities, and secondly, they miss a lot of classes and lose their right to take the exam, respectively. This may be because when students come to study,activities may not be interesting or not relevant to their needs. The teacher's teaching style may not be interesting, or the chosen field of study may not match the student's aptitude (Shiet al.,2015). The results show that cumulative dropout dropping out is significantly correlated with low academic performance, high opportunity cost, low socio-economic status, and poor mental health (Fortin et al.,2006). The importance of behavior problems and learning difficulties while emphasizing the significance of both depression and the family and classroom environments in the development of dropout risk (Ivan et al.,2012). Students consider dropping out of school because they feel they have been mistreated or taught harshly. Useless does not prepare them for college enrollment because working while studying is a part of their lives, they won't have to abandon it. But they will find it difficult to stay motivated to study in college. In the end, the opportunity to graduate will decrease andimpact student attrition.
Educational institutions should implement a student support system that includes teacher advisers to address the issue of scholarship students slipping out of the system. Students must convene every week. It is crucial to closely monitor students who are struggling academically and provide additional instruction to support their learning. This approach aligns with the findings of Urbina-Nájeraet al. (2020), who develop mechanisms to facilitate the provision of counseling services. Implementing initiatives that improve service quality, such as involving senior students in mentoring incoming first-year students, can help achieve this goal. Similarly, teachers should provide personalized tutoring to address academic challenges and identify areas of weakness or potential problems, directing pupils to the right support services. Saengkhunnatham and Prajongjit (2023) found that students must exhibit self-discipline when managing their time and possess a clear understanding of the significance of learning. Regular follow-up is essential. To provide prompt guidance, it is essential to conduct home visits with pupils. The family unit must actively collaborate and routinely communicate with teachers and educational establishments. Muchlisinet al. (2020)express their opinion that educators must demonstrate ingenuity in presenting instructional information. To enhance student achievement, it is essential to impart knowledge to students and optimize their success. For instance, if students possess entrepreneurial talents, it is imperative to offer training specifically tailored to this area. There are sufficient educational resources available. Additionally, there is a designated opportunity for reviewing the material after each class session. To ensure comprehension of the educational materials, pupils who have a low attendance rate will require additional support from the teaching faculty. Meryemet al. (2024)said that it is essential to adopt a proactive strategy within the school ecology. To effectively address school dropout, it is necessary to enhance the overall school environment, eradicate violence, and offer targeted assistance in the presence of school psychologists and assistants. Bost and Riccomini (2006) said that the year using effective instructional design and delivery as a primary approach to keeping pupils in school seems to be a subtle yet effective strategy for preventing dropouts. There are significant limitations in addressing the problem of student dropouts in the education system throughout the country. The Ministry of Education has a clear policy aimed at preventing students from leaving school. However, some educational institutions still experience high dropout rates. One reason for this issue is that many students are not prepared to enter the education system, and their families may not support their educational pursuits. Additionally, some administrators and teachers in these institutions do not prioritize preventing dropouts. This lack of attention and importance given to the issue contributes to the ongoing problem of students leaving the education system.
The objective is to establish a comprehensive support system for vocational students, with a focus on addressing the risk factors associated with dropping out. The system comprises four key components: Component 1: Living Care; Component 2: Dropout Protection; Component 3: Counseling and Advising; and Element 4: Transfer to Support. Given the disadvantaged backgrounds of Equality Education Scholarship recipients, who come from underprivileged families with limited societal opportunities, it is crucial to provide them with specialized care and attention. Colleges need to prevent students from abruptly ending their education before fulfilling their graduation requirements. We should promote and prepare vocational courses to alleviate the financial strain on families. To improve the academic proficiency of students from impoverished households, multiple sectors must collaborate. By providing support and assistance to students, we aim to enhance their physical, mental, and intellectual capabilities, thereby ensuring high quality. One significant aspect of growth involves incorporating morality and ethics and promoting a happy lifestyle as desired by society. Additionally, it is crucial to prevent and address various issues that pupils encounter. As a result of significant changes in social conditions, several technologies align with the opinions ofPraraksa(2021). The project involved the creation of a system for managing student support services. We executed the project through four key activities: development, assistance, sales promotion, and additions, Pholyiam, C. et al. (2024). Nine aspects influence disadvantaged students' quality of life growth; one of them is the student care and support system. These aspects include considerations related to safety systems in educational institutions, factors that enhance the quality of education, and elements that contribute to the establishment of equal opportunities and equity in education across all age groups. The physical health elements of students include social interactions, educational organization for career skill development and capability enhancement, student mental development factors, and environmental factors. These factors were discussed by Anderson et al. (2020), a competent teacher is someone who prioritizes discipline. A teacher who is attentive to instruction and genuinely concerned about their pupils has a significant impact on student engagement in the subject. Banayoet al.(2023) possess a strong passion for acquiring knowledge and are highly motivated by their aspirations for the future. Providing support for groups and academic endeavors. Help scholarship administrators handle issues related to scholarships and the benefits they provide. Walsh, C. et al. (2009) said that it is the year of specialized support systems. This includes career and student financial services. The Student Health Benefits and Counseling Service is the main source of care and support for students.The development of a vocational student care and support system consists of four key components that align with the student care and support systems in educational institutions under the Ministry of Education at the basic education level. This process is systematic and involves clear steps, standardized methods, and tools, and produces quality, verifiable evidence of work. Homeroom teachers and advisors play a central role in this operation, with involvement from all personnel both inside and outside the educational institution. This includes the educational institution committee, parents, community members, administrators, all teachers, and external experts, all of whom must follow clear methods and tools and provide verifiable evidence of their work.The student care and support system comprises five essential components:1) Knowing students individually,2) Student screening,3) Prevention and problem-solving,4) Student development and promotion, and 5) Referral. The success of this system fosters awareness among all personnel regarding the importance of student care and support. Furthermore, it allows for effective integration with the educational institution's missions. Educational institutions and parent organizations can access information on the student care and support system, enabling them to monitor, follow up, inspect, and evaluate its operations accurately.
Conclusion
Dropping out of school is a highly intricate and detrimental issue for pupils. Parents and educational institutions, along with their predictive capabilities, can contribute to mitigating social and economic burdens. To address this issue, we have created a tool that utilizes the learning methodologies used in this research. This enables scholarship recipients to anticipate attrition as they begin their first year of academic pursuit. This study provides a comprehensive care and support system for vocational students, serving as a valuable resource to enhance and advance students' lives at educational institutions. It serves as a means for progress and advancement. Take care of students' physical, mental, intellectual, social, moral, and ethical development. Educational institution administrators and personnel gather information about students to gain a deeper understanding of them and their academic progress. Screening students enables the identification of potential issues and allows for appropriate intervention. This helps to promote students' well-being, and prevent, and address various difficulties. Additionally, we can forward any arising issues to the appropriate agencies for resolution. Consequently, instructors and personnel get enhanced knowledge and understanding, making them better equipped to effectively manage the student care and assistance system.
Summary of the impact of support systems on student dropouts: A well-structured support system that includes effective counseling can guide students in choosing career paths that align with their abilities and interests. This alignment boosts students' confidence and motivation to study. Additionally, programs that help develop essential career skills—such as teamwork, communication, and problem-solving—further enhance students' self-esteem and their ability to pursue a career. Moreover, teachers who provide encouragement and support can help alleviate the stress and pressure associated with studying, contributing to a safer and more positive learning environment for students. Regular monitoring of student's progress also ensures that they do not feel isolated; it offers them the opportunity to improve and receive assistance in areas where they may be struggling.
Recommendations
The study found that the reasons why scholarship students drop out of the education system depend on risk factors in the teaching and learning process. Educational institutions that will use the study results There should be a method for filtering basic information and selecting students who are ready for intensive study before entering school, are motivated to study, and are attentive to their studies. Educational institutions need to hire psychologists or counselors to provide counseling to students with mental problems to reduce the risk of students dropping outand solving various problems. In addition, the school should organize activities to help students and their families so that students and parents can trust the school, resulting in students having love, attachment, and loyalty to the school. This will effectively and efficiently reduce the risk of students dropping out.
Limitations
This study collected data from only the educational institutions that received the Advanced Vocational Innovation Grant with a relatively high level of students dropping out. Data could not be collected from all vocational educational institutions because the educational institutions that received the Advanced Vocational Innovation Grant had conditions for developing care and providing assistance to students who received the grant to prevent them from dropping out during their studies. Therefore, the limitations of this research are, firstly, that collecting data from high-risk educational institutions requires a limited amount of data. Secondly, collecting data from students who had already dropped out of school was quite difficult because students moved with their families and some students did not provide information on the reasons for dropping out, resulting in incomplete data collection for all students.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Education Equality Fund through the Enrichment, Monitoring, and Evaluation Project for Vocational Education Institutions Receiving Higher Vocational Innovation.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Ethics Statements
This study focuses on the author’s experiences, and no other human beings studied.

